what gas is necessary for consumers to carry out life processes
Chapter 5: Introduction to Photosynthesis
five.i: Overview of Photosynthesis
Learning Objectives
By the terminate of this section, yous will be able to:
- Summarize the process of photosynthesis
- Explain the relevance of photosynthesis to other living things
- Identify the reactants and products of photosynthesis
- Draw the main structures involved in photosynthesis
All living organisms on world consist of ane or more cells. Each prison cell runs on the chemic energy found mainly in sugar molecules (food), and the majority of these molecules are produced by 1 process: photosynthesis. Through photosynthesis, certain organisms convert solar energy (sunlight) into chemical energy, which is and then used to build carbohydrate molecules. The energy used to concur these molecules together is released when an organism breaks down food. Cells and then use this energy to perform work, such equally cellular respiration.
The energy that is harnessed from photosynthesis enters the ecosystems of our planet continuously and is transferred from one organism to another. Therefore, direct or indirectly, the procedure of photosynthesis provides most of the free energy required by living things on earth.
Photosynthesis also results in the release of oxygen into the atmosphere. In short, to eat and breathe, humans depend almost entirely on the organisms that carry out photosynthesis.
Concept in Action

Click the post-obit link to learn more most photosynthesis.
Solar Dependence and Food Production
Some organisms can carry out photosynthesis, whereas others cannot. An autotroph is an organism that can produce its own food. The Greek roots of the word autotroph hateful "self" (car) "feeder" (troph). Plants are the all-time-known autotrophs, only others exist, including certain types of bacteria and algae (Figure 5.2). Oceanic algae contribute enormous quantities of food and oxygen to global food chains. Plants are too photoautotrophs, a blazon of autotroph that uses sunlight and carbon from carbon dioxide to synthesize chemical free energy in the form of carbohydrates. All organisms carrying out photosynthesis crave sunlight.

Heterotrophs are organisms incapable of photosynthesis that must therefore obtain energy and carbon from food by consuming other organisms. The Greek roots of the word heterotroph mean "other" (hetero) "feeder" (troph), meaning that their food comes from other organisms. Even if the food organism is another animal, this food traces its origins back to autotrophs and the process of photosynthesis. Humans are heterotrophs, as are all animals. Heterotrophs depend on autotrophs, either directly or indirectly. Deer and wolves are heterotrophs. A deer obtains energy past eating plants. A wolf eating a deer obtains energy that originally came from the plants eaten by that deer. The energy in the plant came from photosynthesis, and therefore information technology is the only autotroph in this example (Figure 5.3). Using this reasoning, all food eaten by humans likewise links dorsum to autotrophs that carry out photosynthesis.

Biology in Action
Photosynthesis at the Grocery Store

Major grocery stores in the United states of america are organized into departments, such as dairy, meats, produce, breadstuff, cereals, and then forth. Each alley contains hundreds, if non thousands, of dissimilar products for customers to buy and eat (Figure five.4).
Although there is a big variety, each item links dorsum to photosynthesis. Meats and dairy products link to photosynthesis because the animals were fed constitute-based foods. The breads, cereals, and pastas come largely from grains, which are the seeds of photosynthetic plants. What about desserts and drinks? All of these products contain sugar—the basic carbohydrate molecule produced directly from photosynthesis. The photosynthesis connexion applies to every meal and every food a person consumes.
Main Structures and Summary of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis requires sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water as starting reactants (Figure v.5). Later the process is consummate, photosynthesis releases oxygen and produces carbohydrate molecules, almost commonly glucose. These sugar molecules comprise the energy that living things need to survive.
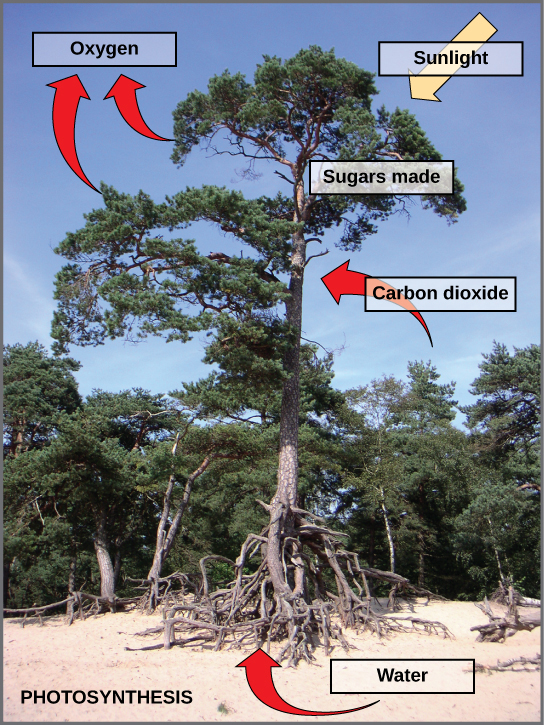
The complex reactions of photosynthesis can be summarized by the chemical equation shown in Figure 5.6.
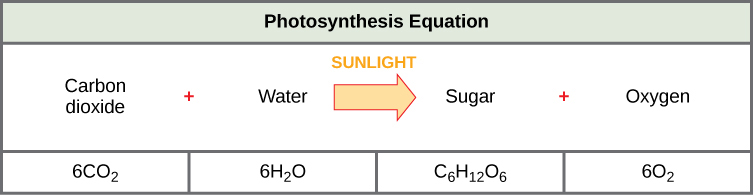
Although the equation looks uncomplicated, the many steps that take identify during photosynthesis are actually quite complex, as in the way that the reaction summarizing cellular respiration represented many individual reactions. Before learning the details of how photoautotrophs turn sunlight into food, it is important to go familiar with the physical structures involved.
In plants, photosynthesis takes place primarily in leaves, which consist of many layers of cells and have differentiated height and lesser sides. The procedure of photosynthesis occurs not on the surface layers of the leaf, but rather in a middle layer called the mesophyll (Figure 5.seven). The gas exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen occurs through small, regulated openings chosen stomata.
In all autotrophic eukaryotes, photosynthesis takes place inside an organelle called a chloroplast. In plants, chloroplast-containing cells exist in the mesophyll. Chloroplasts have a double (inner and outer) membrane. Within the chloroplast is a third membrane that forms stacked, disc-shaped structures called thylakoids. Embedded in the thylakoid membrane are molecules of chlorophyll, a pigment (a molecule that absorbs calorie-free) through which the entire procedure of photosynthesis begins. Chlorophyll is responsible for the green color of plants. The thylakoid membrane encloses an internal space called the thylakoid space. Other types of pigments are too involved in photosynthesis, but chlorophyll is past far the most important. As shown in Figure 5.7, a stack of thylakoids is chosen a granum, and the space surrounding the granum is called stroma (not to be dislocated with stomata, the openings on the leaves).
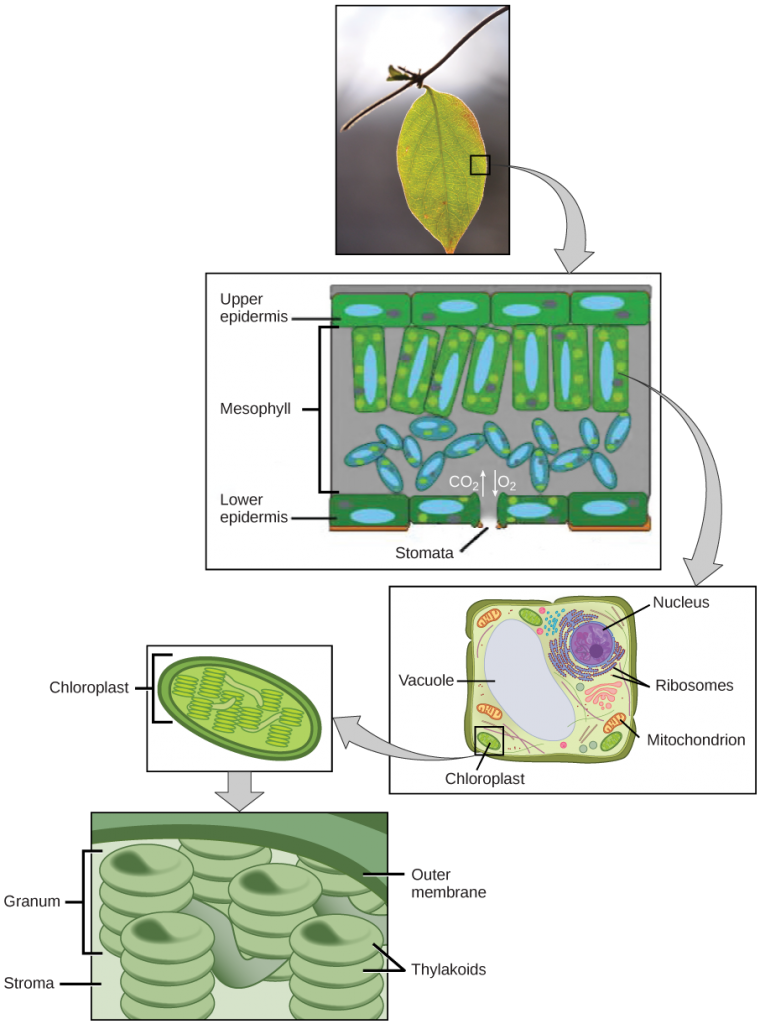
On a hot, dry twenty-four hour period, plants close their stomata to conserve h2o. What bear on will this have on photosynthesis?
The 2 Parts of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis takes place in two stages: the lite-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle. In the light-dependent reactions, which take place at the thylakoid membrane, chlorophyll absorbs free energy from sunlight and and so converts it into chemic energy with the employ of water. The light-dependent reactions release oxygen from the hydrolysis of water as a byproduct. In the Calvin bike, which takes place in the stroma, the chemical energy derived from the light-dependent reactions drives both the capture of carbon in carbon dioxide molecules and the subsequent assembly of saccharide molecules. The two reactions use carrier molecules to transport the energy from ane to the other. The carriers that move energy from the calorie-free-dependent reactions to the Calvin bicycle reactions can be thought of as "full" because they bring energy. Later the energy is released, the "empty" energy carriers return to the light-dependent reactions to obtain more energy.
Section Summary
The process of photosynthesis transformed life on earth. By harnessing energy from the sun, photosynthesis allowed living things to admission enormous amounts of energy. Considering of photosynthesis, living things gained access to sufficient energy, assuasive them to evolve new structures and attain the biodiversity that is evident today.
But certain organisms, called autotrophs, can perform photosynthesis; they crave the presence of chlorophyll, a specialized pigment that can absorb low-cal and catechumen light energy into chemical energy. Photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide and h2o to assemble carbohydrate molecules (usually glucose) and releases oxygen into the air. Eukaryotic autotrophs, such equally plants and algae, have organelles chosen chloroplasts in which photosynthesis takes place.
Glossary
autotroph: an organism capable of producing its own nutrient
chlorophyll: the green pigment that captures the lite energy that drives the reactions of photosynthesis
chloroplast: the organelle where photosynthesis takes place
granum: a stack of thylakoids located inside a chloroplast
heterotroph: an organism that consumes other organisms for food
light-dependent reaction: the first stage of photosynthesis where visible light is absorbed to form ii energy-conveying molecules (ATP and NADPH)
mesophyll: the middle layer of cells in a leaf
photoautotroph: an organism capable of synthesizing its ain food molecules (storing energy), using the energy of lite
pigment: a molecule that is capable of absorbing light energy
stoma: the opening that regulates gas substitution and water regulation between leaves and the surround; plural: stomata
stroma: the fluid-filled space surrounding the grana inside a chloroplast where the Calvin cycle reactions of photosynthesis take place
thylakoid: a disc-shaped membranous structure inside a chloroplast where the low-cal-dependent reactions of photosynthesis take place using chlorophyll embedded in the membranes
Source: https://opentextbc.ca/biology/chapter/5-1-overview-of-photosynthesis/
0 Response to "what gas is necessary for consumers to carry out life processes"
Post a Comment